summary
Using the Change Data Capture (CDC) method from PostgreSQL's WAL, only data that has changed can be identified and transferred to BigQuery. This will result in reduced transfer volume and faster transfers.
Full Data Transfer must be done on the first run. Subsequently, in Incremental Data Transfer, only the Incremental Data Transfer is linked using the CDC method.
When using PostgreSQL CDC
-
You must create your own replication slots for each ETL Configuration (for each table to be forwarded by CDC) by following the instructions.
- Automatic creation and deletion of replication slots is not supported at this time.
- Replication slots are not automatically deleted when ETL Configuration is deleted. Be sure to remember to delete the file.
- If you forget to delete the replication slots, the WAL will overwhelm the storage and may cause the DB to crash.
-
When using PostgreSQL CDC, please make sure that there is enough room for DB storage.
- It is recommended to monitor storage size.
essential condition
PostgreSQL Support Table
| Master | Read Replica | Supported Versions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL RDS | ○ | x | 10.6+ |
| Amazon PostgreSQL RDS | ○ | x | 9.4+ |
| Google CloudSQL PostgreSQL | x | x | |
| Heroku | x | x | |
| PostgreSQL | ○ | x | 9.4+ |
PostgreSQL Parameter Settings
rds.logical_replication= 1 # Set only for RDS.
wal_level=logical # Set if non-RDS.
max_replication_slots= 5 # Set the same number as the tables to be linked.
max_wal_senders= 5 # Set the same number as the tables to be linked.
*It may be necessary to restart DB to reflect WAL settings.
Slot Creation
- A separate Slot must be created for each table to be linked (for each ETL Configuration).
- After logging in as SUPERUSER, create a slot using the SQL below.
*Currently, only wasl2json is supported.
- After logging in as SUPERUSER, create a slot using the SQL below.
SELECT *
FROM pg_create_logical_replication_slot('trocco_<table_name>', 'wal2json');
- The following SQL can be used to check if data can be retrieved from the Slot.
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_changes('<replication_slot_name>', null, null);
Authority of connecting users
- The following permissions are required
CONNECT
Example:
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE <database_name> TO <username>;
USAGE
Example:
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA <schema_name> TO <username>
SELECT
Example:
GRANT SELECT ON <schema_name>.<table_name> TO <username>
rds_replication (RDS only)
Example:
GRANT rds_replication TO <username>
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
After granting the SELECT, all schemas in the database are accessible.
Example:
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA <schema_name> GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO <username>
Primary Key in Data Source table
- The Primary Key must be set in the ETL Configuration for the Data Source table.
- Multiple Primary Keys (Composite Primary Key) are also supported.
Conversion function during transfer
PostgreSQL to BigQuery CDC transfers support the following
- Column Drop
- Column Data Conversion
- Change column name
Data transformation of columns is CAST in BigQuery. So we follow BigQuery's CAST rules.
For more information, please see below.
https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/conversion_rules?hl=ja
metadata
- The following columns will be added and linked to the DWH. Therefore, the following cannot be used for column names
| column name | Description. |
|---|---|
| _trocco_fetched_at | Time the transfer was initiated by torcco's ETL Job. |
- The following also cannot be used as column names because they are used to link data to temporary tables.
| column name | Description. |
|---|---|
| _trocco_deleted | Logical deletion flag. When true, it means that the data has been deleted. |
| _trocco_seq | Guarantee the order of WALs in the transfer |
Data Source PostgreSQL SQL support
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
Schema change (ALTER) behavior
| Schema change operation | SQL Example | Behavior when skimmer tracking is enabled | Behavior when schema tracking is disabled |
|---|---|---|---|
| column addition | ALTER TABLE <table_name> ADD <column_name> <data_type> |
Columns are added to BigQuery. The column type is determined by TROCCO. Note that if a column has a default value, please perform Full Data Transfer since the default value is not reflected in BigQuery. |
Additional columns will not be added to BigQuery. By adding the target column setting in ETL Configuration edit in TROCCO, the column will be added to the BigQuery side. Only records that have been updated after setting a new column will have their values captured. Full Data Transfer must be performed to capture all values. |
| column deletion | ALTER TABLE <table_name> DROP <column_name> |
Deleted columns are not deleted from BigQuery. | Same behavior as when skimmer tracking is enabled |
| column type change | ALTER TABLE <table_name> ALTER <column_name> TYPE <data_type> |
If the modified type is type-changeable, it can continue to be transferred. If an error occurs, a Full Data Transfer must be performed. | Same behavior as when schema tracking is enabled |
| Column Name Change | ALTER TABLE <table_name> RENAME <old_column_name> TO <new_column_name> |
A new column is added to BigQuery with the changed column name. Only records updated after the column name change will have the new column value updated. The value of the column before the column name change is not carried over to the new column after the change. Full Data Transfer must be performed in order to capture everything. Also, columns prior to column renaming are not deleted from BigQuery. |
The changed columns will not be added on BigQuery. The column before the change will have the value NULL for the updated record. |
Unsupported SQL
- The following SQL cannot be caught by WAL and data will not be transferred to DWH correctly.
・TRUNCATE
・DROP
・LOAD
・RENAME
・CASCADING DELETES
・CASCADING UPDATES
・ALTER TABLE ... SET DEFAULT
If the data is already linked and is NULL, it will remain NULL and will not be updated.
PostgreSQL and BigQuery schema types
- In the data type conversion function, data types that can be changed can be converted to the specified type.
- The default response is as follows
| PostgreSQL Data Types | BigQuery Data Types |
|---|---|
| CHARACTER VARYING CHARACTER CIDR CITEXT MACADDR TEXT TIME WITH TIMEZONE TIME WITHOUT TIMEZONE UUID TIME INTERVAL |
STRING |
| BOOLEAN | BOOLEAN |
| BIGINT BIG SERIAL INTEGER SERIAL NUMERIC DECIMAL SMALL INT SMALL SERIAL |
INTEGER |
| DOUBLE PRECISION REAL MONEY |
FLOAT |
| DATE | DATE |
| TIMESTAMP DATETIME TIMESTAMP WITH TIMEZONE TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIMEZONE |
TIMESTAMP |
| GEOGRAPHY GEOMETRY HSTORE JSON JSONB POINT TSRANGE TSTZRANGE BOX PATH |
STRING (STRUCT is currently not supported.) |
Configuration Flow
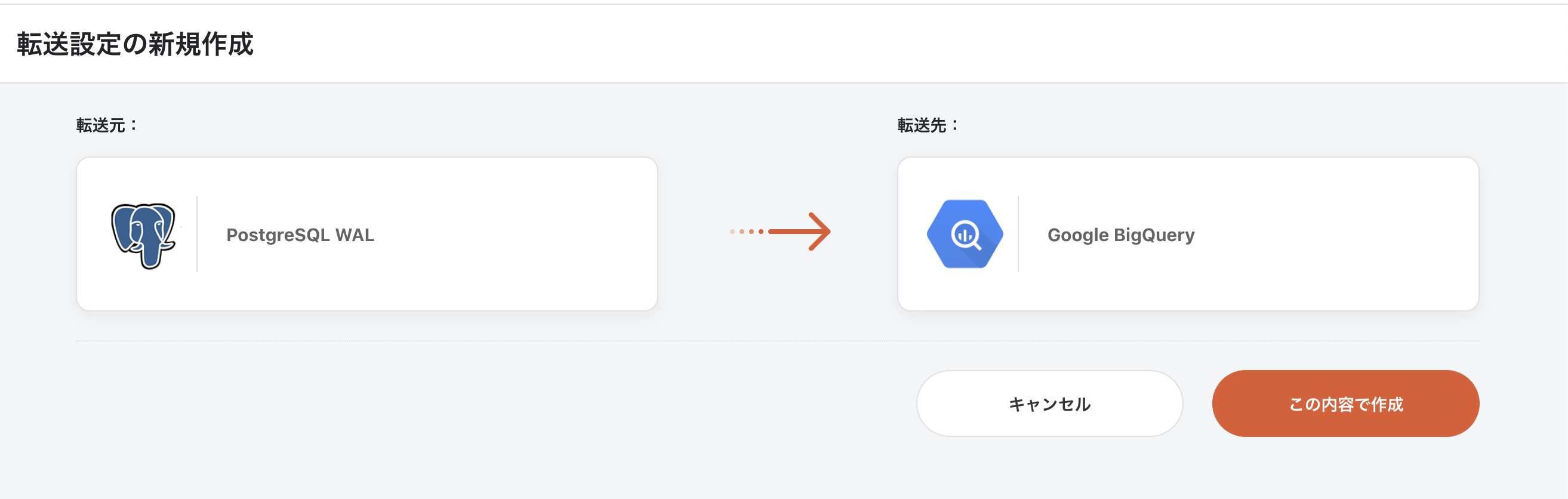
1. create ETL Configuration
Select Data Source PostgreSQL WAL and Data Destination BigQuery and create ETL Configuration.
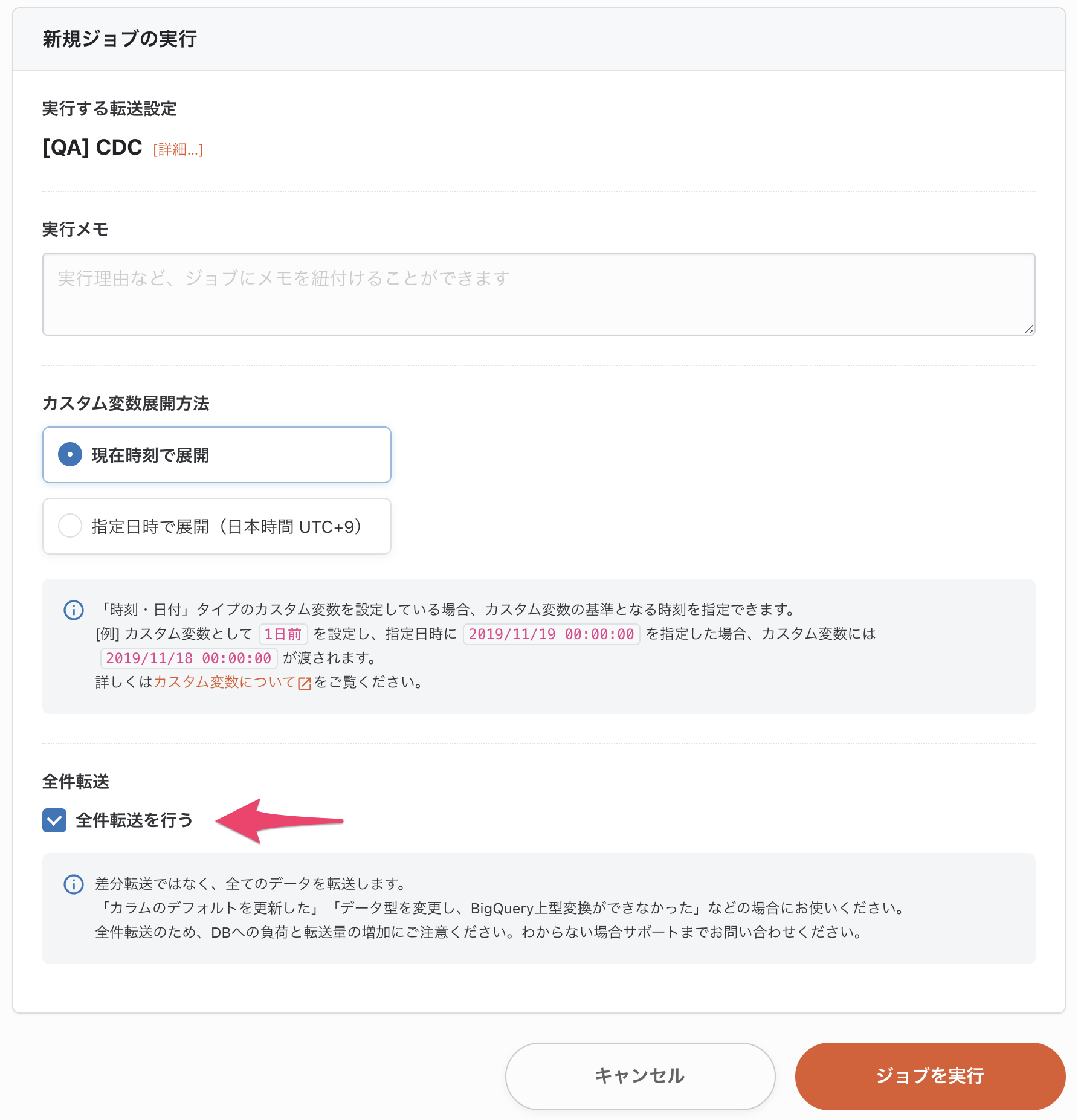
2. initial Full Data Transfer is performed
For the first time only, Full Data Transfer is performed to transfer the current PostgreSQL table to BigQuery.
On the Run New Job screen, check the Do Full Data Transfer checkbox and run the job.
3. schedule ETL Configuration for Incremental Data Transfer
Please register your schedule from the Schedule Setup screen.
A Job will be started at the Job Setting frequency and the differences will be captured.
If Full Data Transfer is required
Full Data Transfer is required in the following cases
- Initial Transfer
- Runtime error with type conversion on BigQuery
- I want to erase all data, not logical deletion.
Delete the transferred table before executing. - If you execute the query described in "SQL Support for Data Source PostgreSQL