summary
This help page explains DataSetting>Programming ETL inSTEP 2 of****ETL Configuration.
Programming ETL allows you to execute a program you have written against data retrieved from the Data Source.
Programming ETL allows for flexible conversion processes that cannot be performed with Template ETL.
Programming ETL is available only for accounts subscribed to the Advanced plan or higher.
Languages Supported
- Python 3.9
- Ruby 3.2
- Ruby 2.7
By default, only the standard library is available.
If you have an external library you would like to use, please contact our Customer Success with the following information
- Official URL of the external library
- Version to be used
For standard libraries, there is no need to make a new request for additional libraries.
Before requesting the addition of a library, please check from the official documentation below whether the library in question is included in the standard library.
constraints
- Only conversion processes can be written in single line units.
- It is not possible to carry over the results of one line of processing to a subsequent line.
- Therefore, it is not possible to describe aggregate processing that spans multiple lines. Please understand that we are not responsible for any loss or damage to your property.
- The memory limit for program execution is approximately 1 GB.
- The generation of the schema when creating or editing ETL Configuration is timed out after 10 minutes of execution.
- On the other hand, there is no timeout setting for Programming ETL during ETL Job Setting.
- A processing time of about 1 minute per line will run without problems.
Template ETL processing is performed first on the Data Destination data.
Programming ETL is then processed.
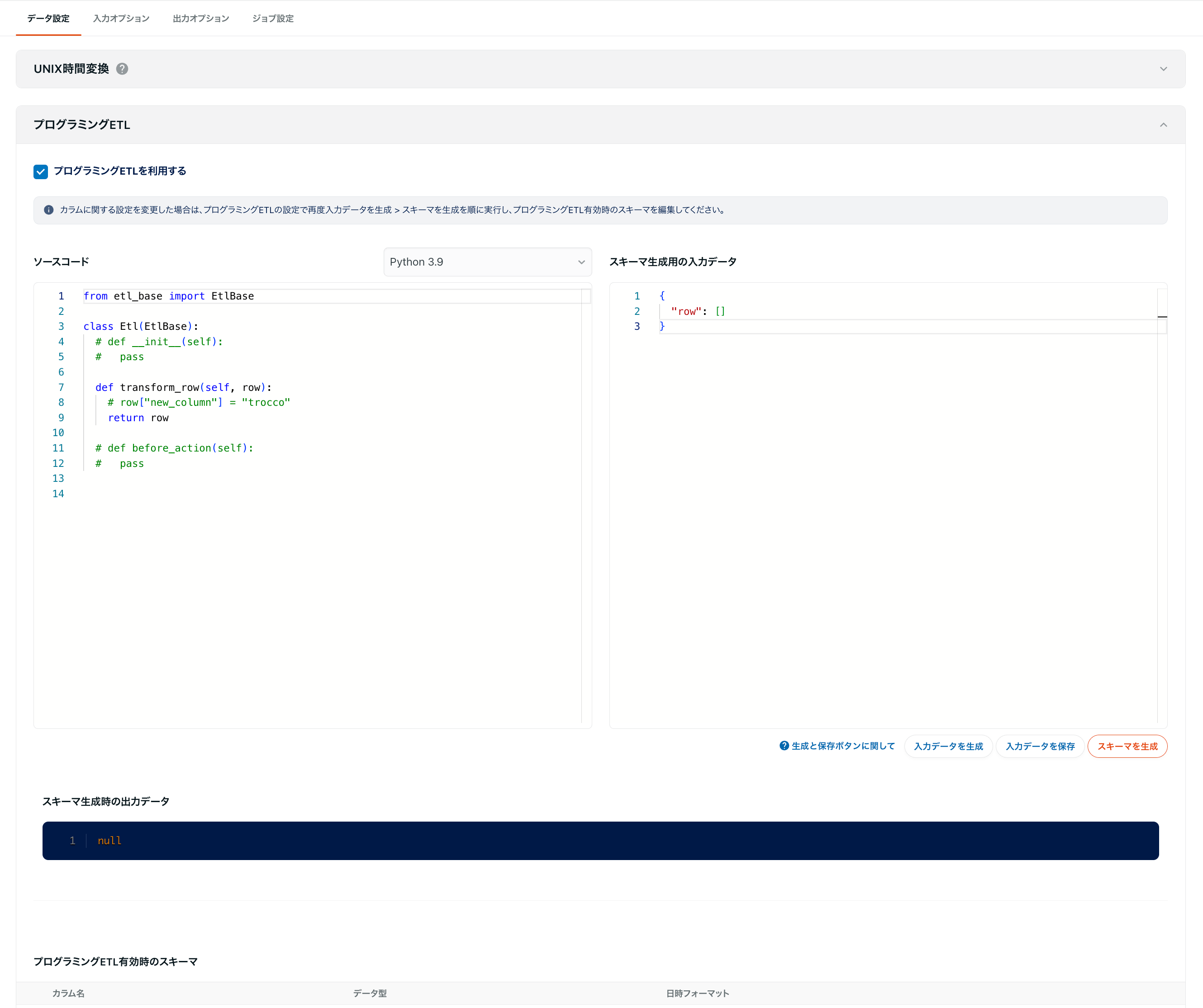
Setup procedure
Programs written in Programming ETL have two roles.
- When creating or editing ETL Configuration, the schema is used to create the schema.
- When an ETL Job is executed, processing is performed on the data acquired from the Data Source.
The following describes the procedure for creating a schema when creating or editing an ETL Configuration.
1. input data generation
Click Generate Input Data.
Data with Template ETL settings reflected will be generated in JSON format in the form of input data for schema generation.
For details, see Format of Input Data for Schema Generation below.
Clicking Save Input Data saves the input data at that point.
After editing input data, you may want to leave the screen and continue editing again.
2. source code description
Write the program in the source code.
For details, see the role of each element in the source code below.
3. schema generation
Click Generate Schema.
The program is executed on the input data generated in step 1.
When execution is complete, data in JSON format is displayed in the output data during schema generation.
The schema will also be updated when Programming ETL is enabled.
Schema generation is designed to time out after 10 minutes of execution.
In the unlikely event of a timeout, edit the source code so that the execution time is within 10 minutes.
Note that this timeout specification is set only for the schema generation process.
There is no time-out setting for Programming ETL during ETL Job Setting.
Editing the schema
Edit the updated Programming ETL enabled schema accordingly.
If you add a date/time string column in the source code, it is recognized as a string type by default.
If you want the date to be recognized as a timestamp type, select the timestamp type in the schema when Programming ETL is enabled, and enter the date and time format as appropriate.
5. schema storage
Click to preview or confirm****changes.
Whichever you click, your Programming ETL settings will be saved.
If you want to see the data with Programming ETL executed, click Preview Changes.
If Programming ETL is disabled, transfers are based on the schema set in the Column Setting.
On the other hand, if Programming ETL is enabled, the transfer is based on the schema when Programming ETL is enabled.
After editing the schema when Programming ETL is enabled, if you have changed the settings regarding columns on the Template ETL side, please perform the configuration procedure again.
Specifications related to programming
Format of input data for schema generation
- Input data is stored in a variable with an array (list) structure
called rows. - Each element of
rowscorresponds to the data in each row, and each element is a hash (dictionary) structure with columns as keys.
rows : [
{<row1_columnA>: <value>,
<row1_columnB>: <value>,
<row1_columnC>: <value>
},
{<row2_columnA>: <value>,
<row2_columnB>: <value>,
<row2_columnC>: <value>
},
{<row3_columnA>: <value>,
<row3_columnB>: <value>,
<row3_columnC>: <value>
}
]
Role of each element in the source code
In the following, Python is used as an example.
from etl_base import EtlBase
class Etl(EtlBase):
def __init__(self):
pass
def transform_row(self, row):
row["columnA"] = "hoge" # Existing column's value is changed.
row["new_column"] = "fuga" # New column is added.
del row["columnC"] # Existing column is deleted.
return row
def before_action(self):
pass
EtlBase and Etl classes
The EtlBase and Etl classes are the necessary elements for executing Programming ETL.
Do not delete or rename.
transform_row method
Please describe the process in this method as appropriate.
When the program is executed, each element of the rows is passed to the transform_row method one row at a time.
By default, each element of rows is passed to row. The following description assumes that row data is passed to row.
- Rewriting the value of a key that exists in
a rowchanges the value of the corresponding column. - Adding a new key to
rowadds a new column with the key name as the column name. - Deleting a key that exists in
a rowdeletes the corresponding column.
Note that the schema is created and transferred based on the return value of the transform_row method.
Therefore, RETURN the processed ROW.
If a NULL value is returned, the transfer of the corresponding line is skipped. ( None for Python and nil for Ruby)
before_action method
It is executed only once, before the transform_row method.
Within the before_action method, instance variables can be assigned.
The value can also be used within the transform_row method.
Use this function when you want to perform arbitrary arithmetic operations before sequential processing of rows.
def before_action(self):
self.hoge = "hoge"
supplementary information
Manual editing of input data for schema generation
Input data for schema generation can also be edited manually.
By editing the input data for schema generation as needed and generating a schema, it is possible to test whether the written program is properly executed.
However, when the****schema is generated, it is also updated when Programming ETL is enabled.
If the structure of the data retrieved from the Data Source at the time the transfer job is executed differs from the schema used when Programming ETL is enabled, the transfer will fail.
Therefore, manual editing of input data for schema generation should be used only as a test.
Standard output/Error output
If an output function/method such as print is written in the source code, its output result will be displayed in the standard output/error output.
Note that error messages will also be displayed in the standard output/error output if the schema generation fails.